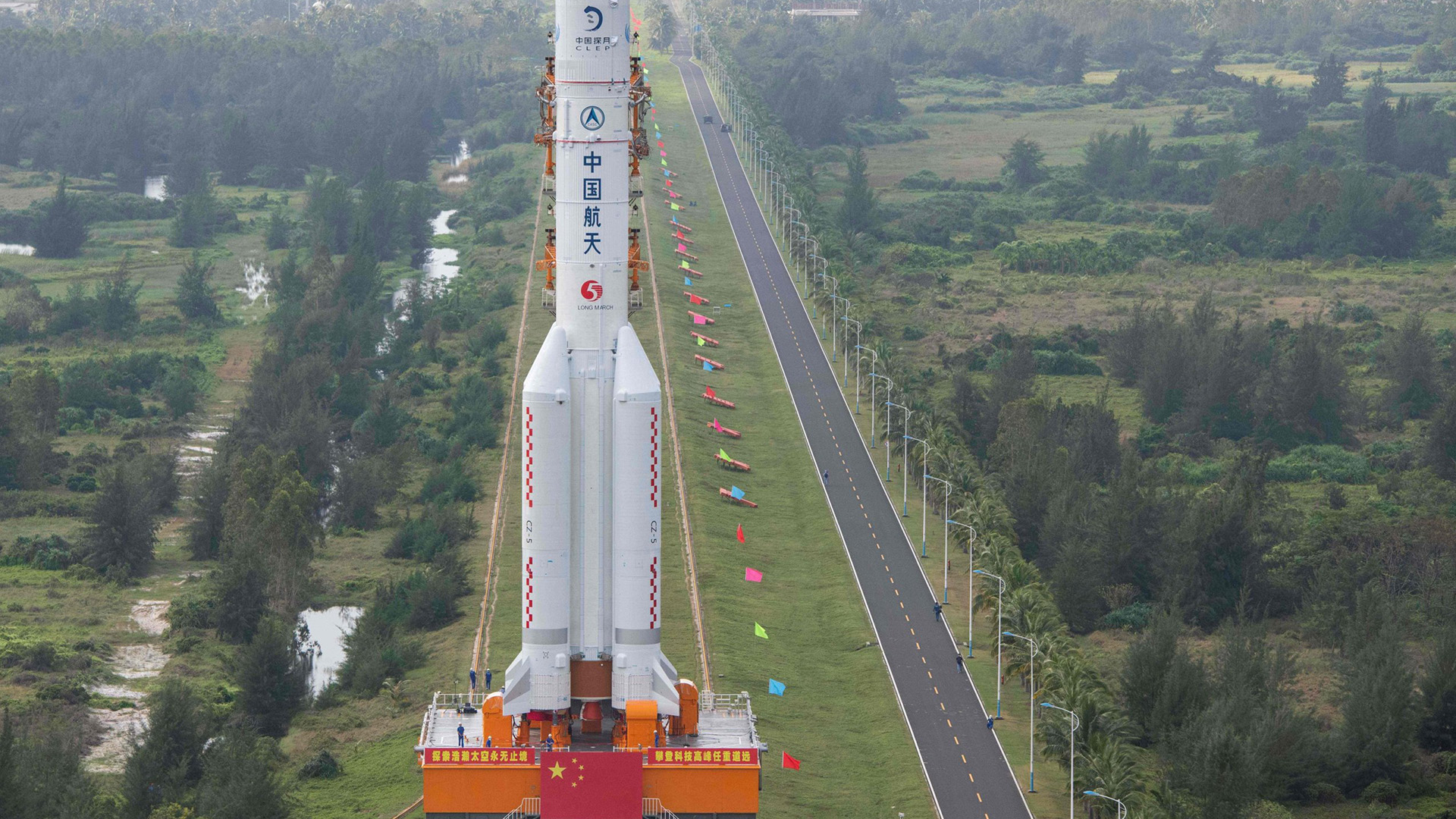
Air and Space Forces — In its annual report to Congress, the U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission highlights China’s “aggressive long-term, whole-of-government campaign” to gain an edge over the U.S. in space. “In just 10 years, China has dramatically transformed an almost nonexistent commercial space sector into a thriving, state-orchestrated startup ecosystem.”
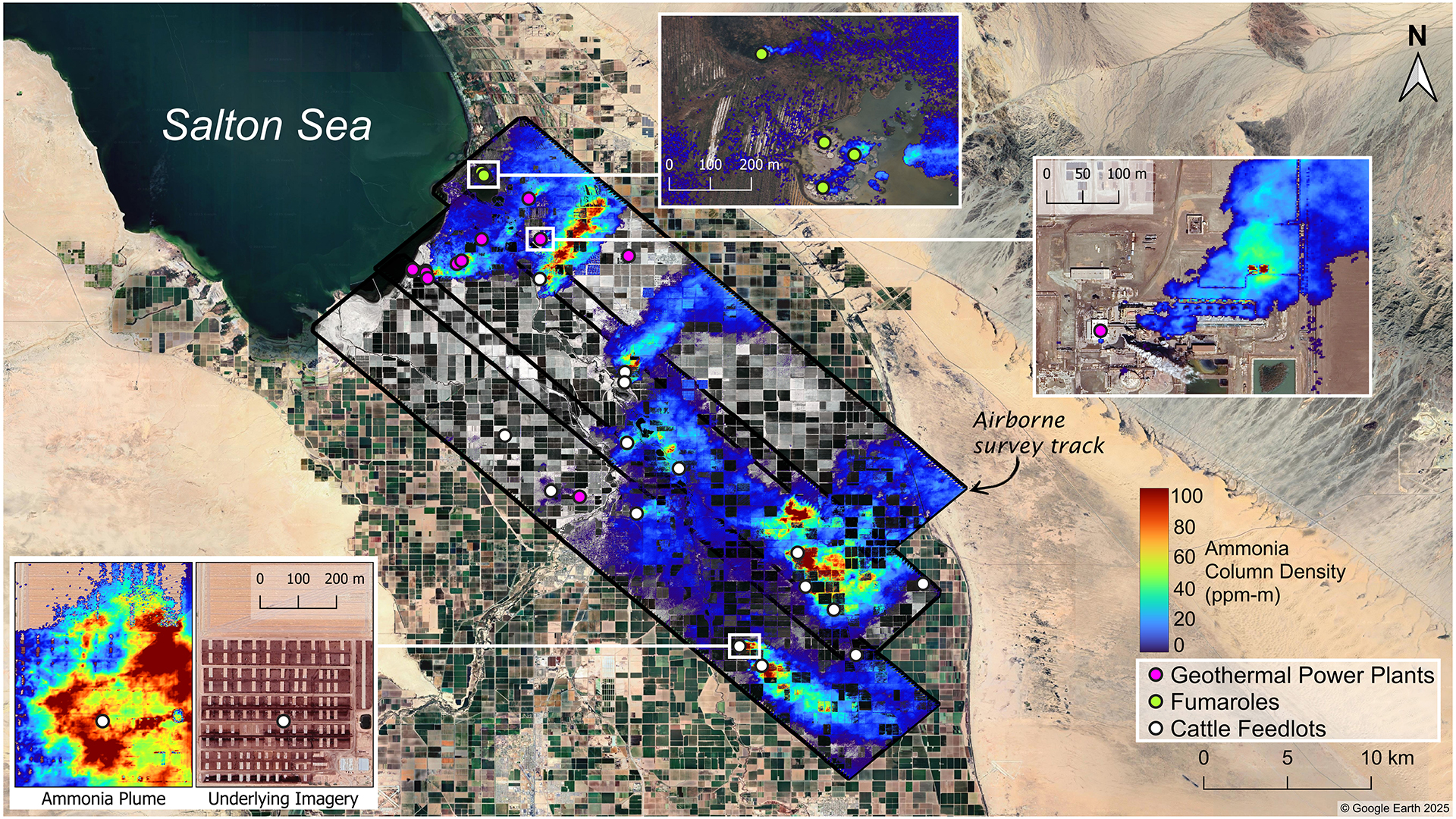
NASA, Aerospace Corporation Study Sharpens Focus on Ammonia Emissions
Space Daily — Aerospace’s David Tratt, who co-authored the paper, said: “We ended up with maps that identify multiple sources of ammonia, and we were able to track the plumes from their sources and observe them coalescing into larger clouds.”
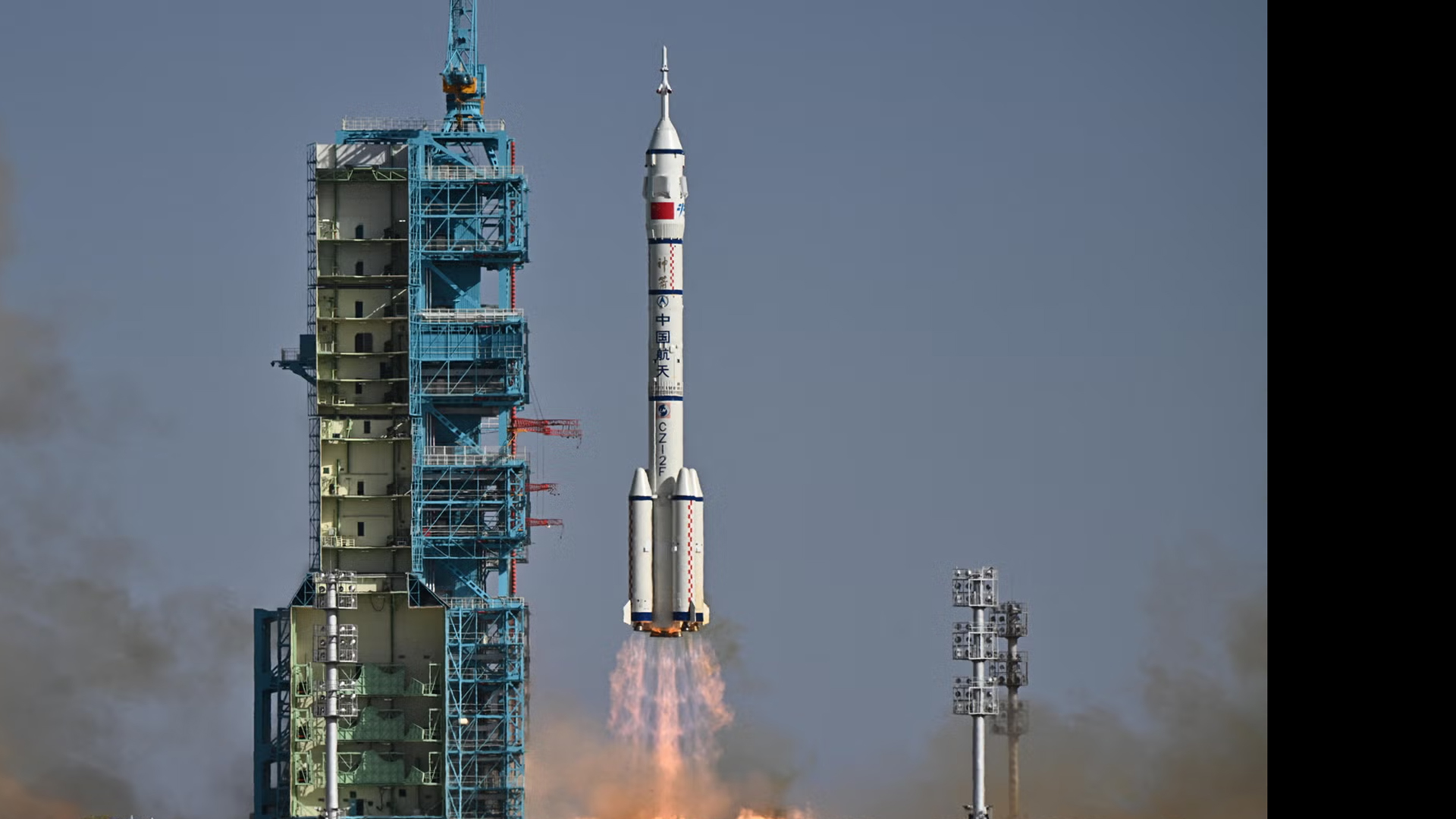
Space Junk Strike on China’s Astronaut Capsule Highlights Need for a Space Rescue Service, Experts Say
Space.com — Aerospace’s Grant Cates (senior project leader in launch operations for the Space Safety Institute), Marlon Sorge (executive director of the Center for Orbital and Reentry Debris Studies (CORDS)), and Brian Weeden (director of civil and commercial policy at the Center for Space Policy and Strategy) all commented on an incident where a suspected impact of space debris cracked a window on China’s Shenzhou 20 crew’s return vessel.
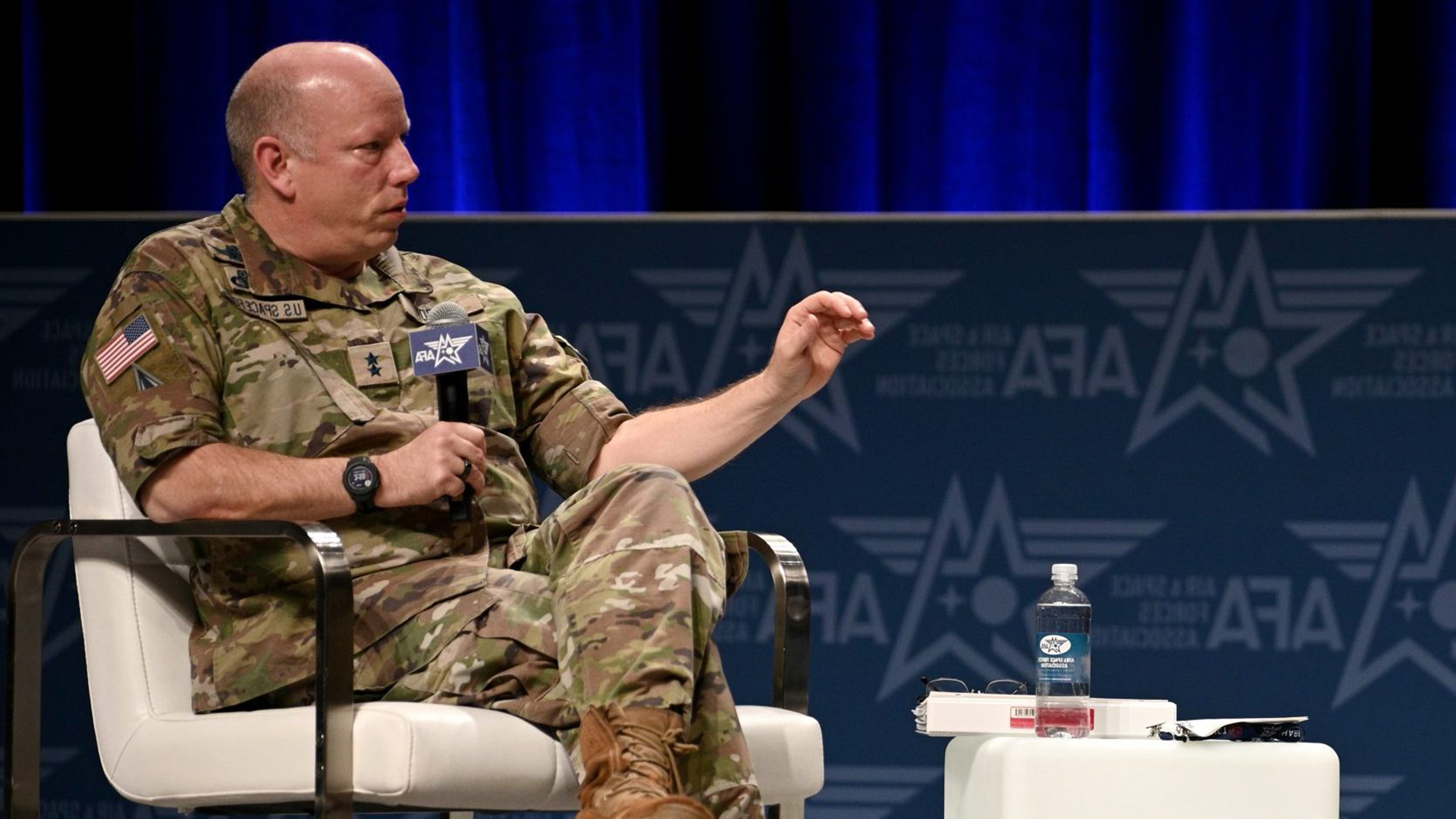
Purdy: Space Force Needs More Acquisition Experts to Implement Reforms
Air and Space Forces — U.S. Space Force’s acting acquisition executive, Maj. Gen. Stephen Purdy, said: “We have a strong, motivated force, but there have been an incredible amount of pressures on them in this past year. … We are in a situation where we barely have enouch acquirers to do all the work that we have now.”
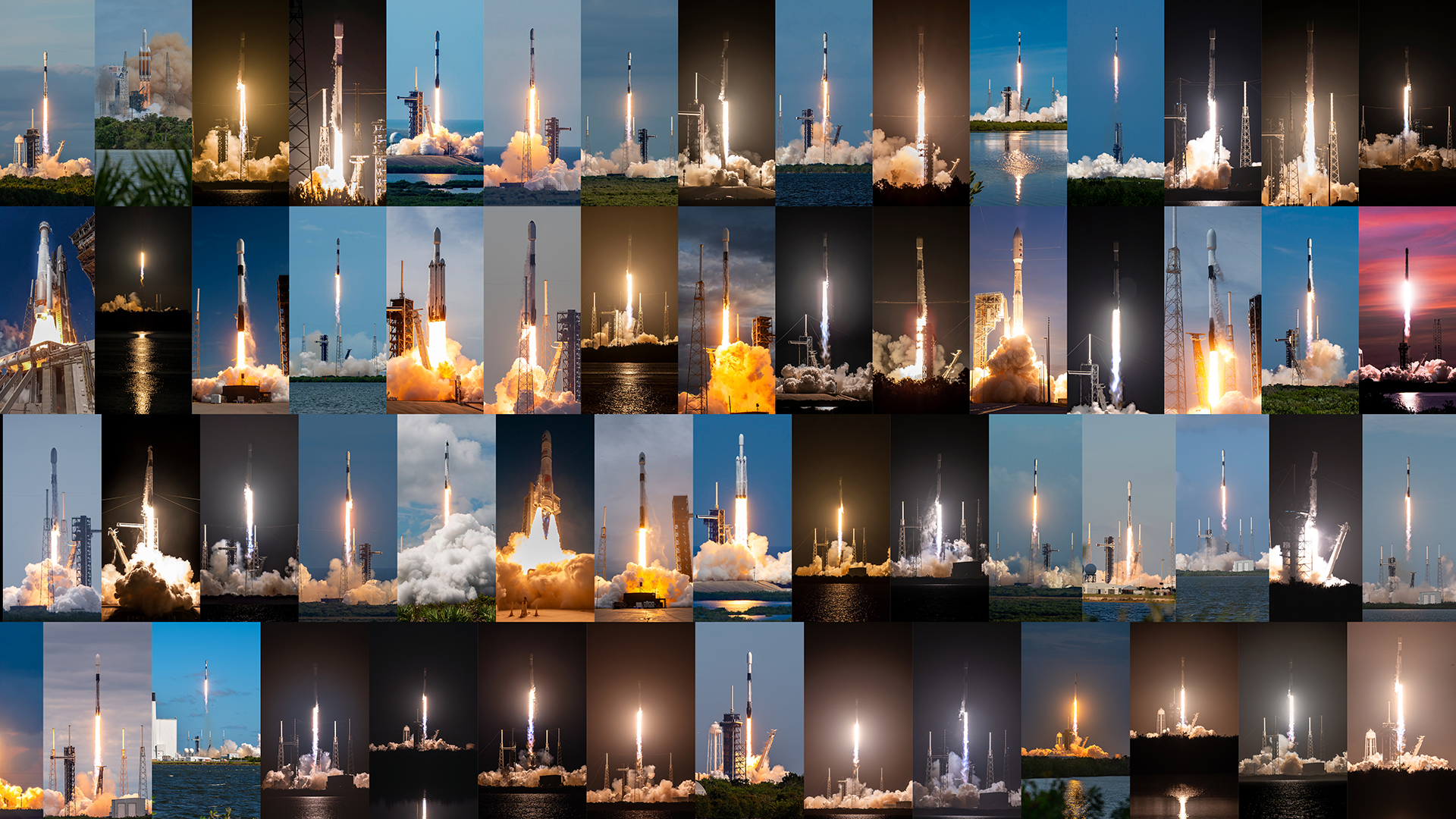
Florida Space Coast Tops 100 Launches as Space Force Pushes for Range Upgrades
SpaceNews — The Starlink mission marked the 100th orbital launch of the year, the first time Cape Canaveral and Kennedy Space Center have ever seen triple-digit activity in a single calendar year. Col. Brian Chatman: The volume is here to stay. The next step is making sure the infrastructure can keep up.
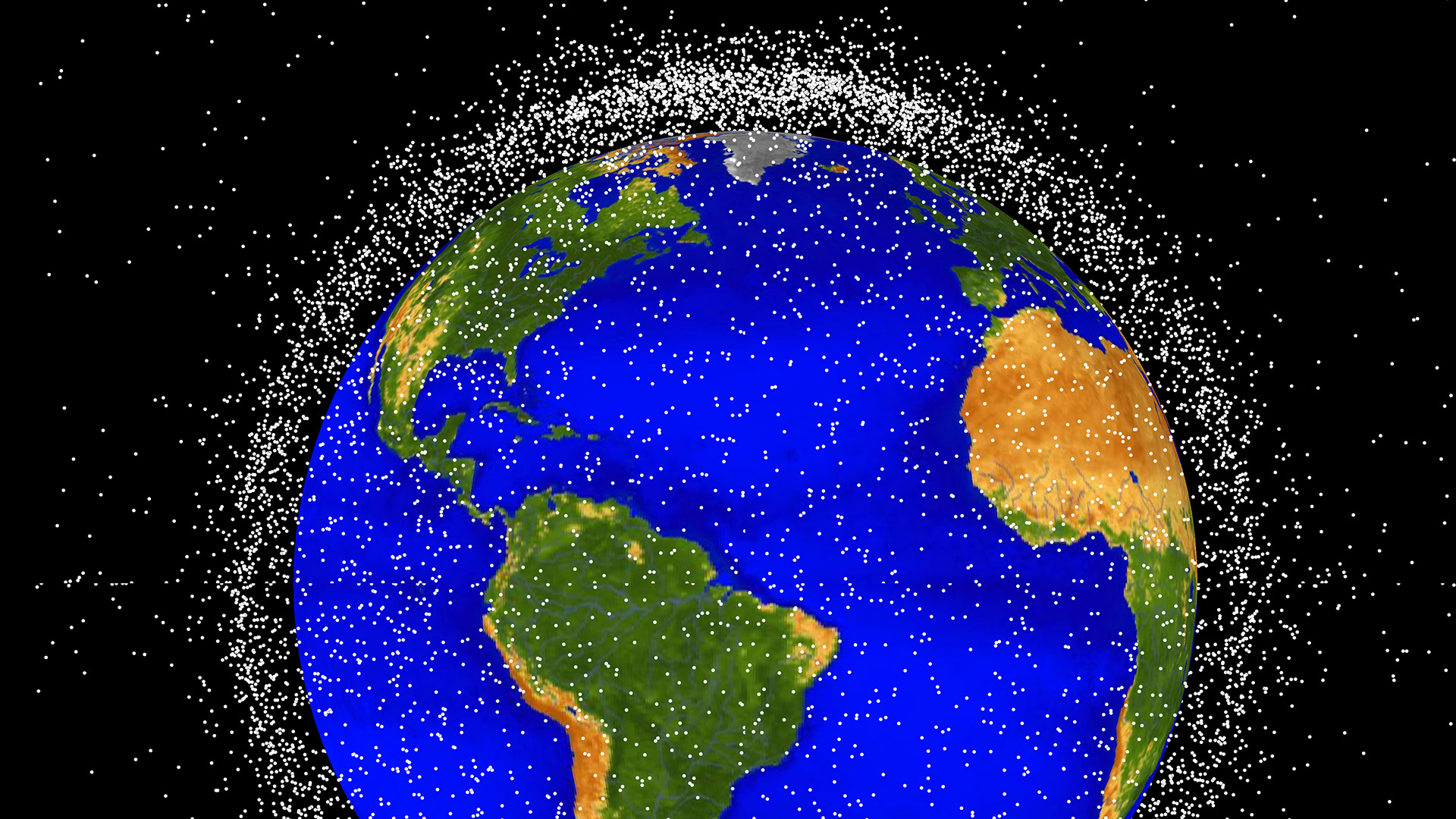
Debris Mitigation Report: Sustainability in Earth Orbit
Reuters — Marlon Sorge, Aerospace’s executive director of the Center for Orbital and Re-entry Debris Studies (CORDS), says the easiest way for operators to ensure they don’t fall foul of the FCC’s 2022 rule that satellites de-orbit within 5 years, is to adhere to the de-orbiting parameters from the start of the design process.
Winning the Space-Cyber War Requires Continuous Investment, Vigilance, and Collaboration
Via Satellite — Aerospace’s Jim Myers, in an opinion piece: “Without continuous testing and adaptation, the space assets critical to preserving our national security and economic prosperity risk becoming fatal vulnerabilities.”
New Cybersecurity Rules for Pentagon’s Commercial Satellite Vendors
Air and Space Forces — Aerospace’s Brandon Bailey told CyberSat conference attendees about new rules from the the Pentagon-led interagency Committee on National Security Systems, which commercial satellite operators must employ if their products or services are used by U.S. intelligence agencies or military services.
Multi-Orbit Networks Expand the Attack Surface, But Basic Cyber Threats Remain, Experts Say
Via Satellite — A recent study found that roughly half of the traffic from Geostationary Orbit (GEO) satellites is still unencrypted. One of Aerospace’s cybersecurity experts, Brandon Bailey, said, “We have too much trust built into our architectures, into that trusted link between the ground and the spacecraft.”
Attack, Defend, Pursue—the US Space Force’s New Naming Scheme Foretells New Era
Ars Technica — The document, titled Space Force Instruction 16-403, covers Space Force weapon system naming and designations, including “A for Attack,” “B for Battle Management,” and “P for Pursuit.”